bind、call 和 apply 能否改变箭头函数的 this 指向?
答案是否定的。箭头函数的 this 值在定义时就已经确定(词法作用域绑定),无法通过 bind、call 或 apply 改变。这是箭头函数与普通函数的核心区别之一。
详细解释与代码验证
1. 基本行为验证
const arrowFunc = () => {
console.log(this); // 始终指向定义时的上下文(此处为全局对象)
};
const context = { value: 42 };
// 尝试改变 this 指向
arrowFunc.call(context); // 输出全局对象(非 context)
arrowFunc.apply(context); // 输出全局对象(非 context)
arrowFunc.bind(context)(); // 输出全局对象(非 context)2. 不同环境下的表现
| 调用方式 | 普通函数 | 箭头函数 |
|---|---|---|
| 直接调用 | window 或 global | 定义时的上下文 |
| 对象方法 | 调用对象 | 定义时的上下文 |
| call/apply | 第一个参数指定的对象 | 定义时的上下文(忽略参数) |
| bind | 绑定的对象 | 定义时的上下文(忽略绑定) |
3. 深入测试案例
// 案例 1:对象方法中的箭头函数
const obj = {
value: "对象属性值",
regularMethod: function() {
console.log("普通方法:", this.value);
},
arrowMethod: () => {
console.log("箭头方法:", this.value);
}
};
obj.regularMethod(); // "普通方法: 对象属性值"
obj.arrowMethod(); // "箭头方法: undefined"(this 指向全局)
// 案例 2:尝试强制绑定
const boundRegular = obj.regularMethod.bind({ value: "绑定的值" });
boundRegular(); // "普通方法: 绑定的值"
const boundArrow = obj.arrowMethod.bind({ value: "绑定的值" });
boundArrow(); // "箭头方法: undefined"(绑定无效)
// 案例 3:嵌套环境测试
function outer() {
const innerArrow = () => console.log("嵌套箭头:", this);
return {
callInner: function() {
innerArrow.call({ attempt: "尝试改变" });
}
};
}
const ctx = { name: "外部上下文" };
const nested = outer.call(ctx);
nested.callInner(); // "嵌套箭头: { name: '外部上下文' }"(call 无效)技术原理分析
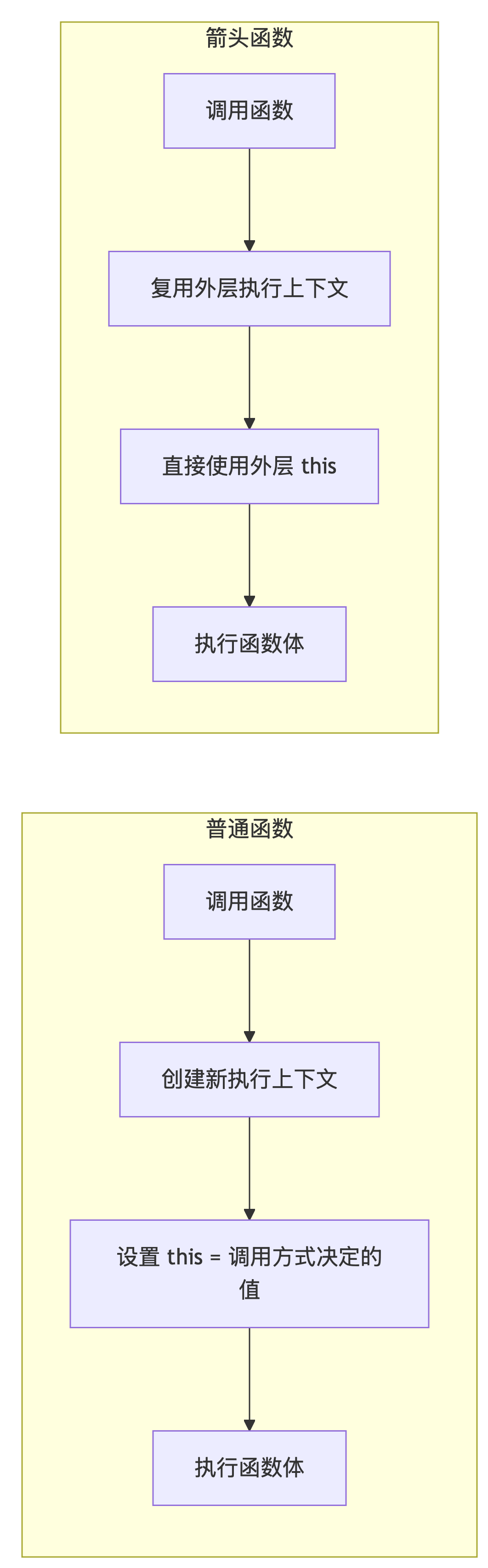
为什么无法改变?
箭头函数没有
this绑定:- 普通函数有内部的
[[ThisValue]]属性存储this - 箭头函数没有此属性,依赖词法作用域的
this
- 普通函数有内部的
执行上下文差异:
// 普通函数的伪实现 function regularFunc() { // 引擎内部:this = ExecutionContext.ThisValue } // 箭头函数的伪实现 const arrowFunc = () => { // 引擎内部:this = LexicalEnvironment.ThisValue }规范定义:
根据 ECMAScript 规范:
- 普通函数调用时创建新的
this绑定 - 箭头函数执行时使用外层执行上下文的
this
- 普通函数调用时创建新的
内存模型对比
实际应用场景
需要动态 this 时(使用普通函数)
// DOM 事件处理
button.addEventListener('click', function() {
console.log(this); // 指向 button 元素
this.classList.toggle('active');
});
// 对象方法
const calculator = {
value: 0,
add: function(num) {
this.value += num;
}
};需要固定 this 时(使用箭头函数)
// 类中绑定实例方法
class Timer {
constructor() {
this.seconds = 0;
this.tick = () => {
this.seconds++; // 始终指向实例
};
}
}
// 异步回调
class DataLoader {
loadData() {
fetch('/api/data')
.then(() => this.processData()); // this 保持为实例
}
}常见误区与解决方案
误区 1:试图在对象方法中使用箭头函数
// 错误用法
const counter = {
count: 0,
increment: () => {
this.count++; // this 指向全局对象
}
};
// 正确解决方案
const counter = {
count: 0,
increment: function() {
this.count++; // 普通函数确保正确 this
}
};
// 或使用简写方法
const counter = {
count: 0,
increment() {
this.count++;
}
};误区 2:在需要动态上下文的回调中使用箭头函数
// 错误用法
const buttons = document.querySelectorAll('button');
buttons.forEach(btn => {
btn.addEventListener('click', () => {
console.log(this); // 指向定义时的上下文(通常全局)
this.classList.add('active'); // 错误!
});
});
// 正确解决方案
buttons.forEach(function(btn) {
btn.addEventListener('click', function() {
this.classList.add('active'); // this 指向按钮元素
});
});关键差异
| 特性 | 普通函数 | 箭头函数 |
|---|---|---|
this 绑定 | 动态绑定(调用时决定) | 词法作用域绑定(定义时确定) |
bind 效果 | 可改变 this 指向 | 无法改变 this |
call/apply 效果 | 可改变 this 指向 | 无法改变 this |
| 构造函数 | 可用作构造函数 | 不可用作构造函数 |
| 适用场景 | 需要动态 this 的场景 | 需要固定 this 的场景 |

Comments | NOTHING